EMR Specification Development Life Cycle
Advancing EMR maturity is a key objective of the ministry’s Patients First: Digital Health Strategy. This objective will help realize the full potential of EMRs to support clinical practice or to share key information needed to improve care coordination; this should include improved interoperability and connection to provincial assets, and increased maturity of EMR use.
Initiatives that result in EMR Specifications arise primarily from provincial and clinical priorities. The Ministry of Health will set priorities informed by the Clinician Digital Health Council.
New or updated EMR Specifications arise from EMR maturity initiatives such as EHR integration, EMR tooling and/or Health Information Exchange. EMR Specifications set expectations and/or minimum requirements for how EMRs should behave in consuming a service or performing a Point of Service function. (e.g.: downloading a drug result). These initiatives will also set and/or leverage common, fundamental provincial standards for EMRs such as identity management, data and messaging standards.
EMR Specifications are a collection of one or more documents that all EMR vendors use to ensure a minimum, common, consistent implementation of requirements in their EMR Offerings.
The development of an EMR Specification is an ongoing process which depends on the collaborative contributions of numerous stakeholders such as clinicians, project sponsors, the Ministry of Health, Ontario Health - Digital Services, EMR vendors, subject matter experts (SMEs) and other stakeholders. As EMR maturity advances, existing EMR specifications will continue to evolve and new ones will be added.
This EMR Specification Development Life cycle overview describes the processes and activities involved.
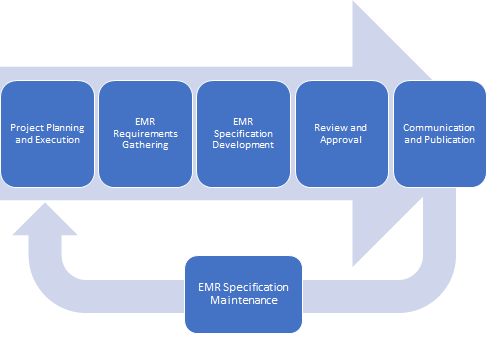
1 Project Planning and Execution
The initial phase of the EMR Specification Development Life Cycle includes defining the scope and activities based on the provincial priorities set by the ministry, Clinician Digital Health Council, clinicians and other stakeholders. A project may be initiated to support updates or new requirements in an EMR Offering needed to advance the mature use of an EMR. These requirements may be new functional or non-functional requirements as well may introduce a new EHR product/service. In this phase, some of the key activities may include:
- Development of the project charter (Scope, objectives, deliverables, timeline, budget etc)
- Identification of the project team (e.g. key stakeholders, sponsors, funders, delivery partners, etc)
All EMR vendors with certified EMR Offerings are informed of the initiative. OntarioMD will often work with a select number of EMR vendors and physicians/practices in a proof of concept to demonstrate the desired objectives, and/or incorporate these requirements into their EMR Offerings'.
2 EMR Requirements Gathering
The purpose of this stage is to concisely capture (functional and non-functional) requirements and relevant information needed from key stakeholders (e.g. clinicians, regulatory bodies, etc) for implementation in an EMR Offering.
EMR requirements may be gathered using various methods, including requirements workshops, surveys, onsite visits and other means.
Each requirement is reviewed by team members for its accuracy, priority, and further refined as necessary.
3 EMR Specification Development
EMR specifications provide a context for implementation of a set of requirements. For example, use case scenarios, integration objectives are packaged into various components for different audiences by providing a business view, implementation, and other components where applicable.
EMR requirements are reviewed to enhance clarity and consistency of language, terminology, formatting and other established documentation styles and standards (e.g., versioning, packaging) across all documents.
Ambiguous EMR requirements are further refined and any redundant requirements already addressed in other existing EMR specifications are removed.
Once EMR requirements have been finalized, a draft EMR specification is produced for broader review and approval.
4 Review and Approval
In the creation or update of an EMR specification, EMR vendors with currently certified EMR Offerings (including those who participated in the demonstration phase) and other stakeholders have an opportunity to review the EMR Specification and requirements within for clarity and understanding prior to publication. The duration of the review period will vary depending on the extent of the EMR specification(s) being reviewed.
Issues raised to OntarioMD through this review period, will be acknowledged and assessed by the project team. Any resulting revisions to the EMR specification will be made available for final review.
Issues that cannot be resolved as part of the EMR Specification review should be escalated through OntarioMD's
Dispute Resolution Process.
5 Communication and Publication
Throughout the lifecycle of the EMR specification EMR vendors with certified EMR Offerings will be updated on progress, timeline, and any anticipated impacts to EMR certification for planning purposes.
For further information about EMR Specifications status, refer to the
EMR Specification Overview
6 EMR Specification Maintenance
EMR Specifications may require updating over time for several reasons, which includes:
- Minor revisions: clarification, formatting, etc
- Major revisions: new/revised requirements
These revisions will be assessed for prioritization in a subsequent version of the EMR Specification and development lifecycle.